The Accelerating Growth of Wind and Solar Energy is Being Driven by Government Climate Policies, Global Corporations Thrusting Themselves onto the Green Bandwagon, Fervent Activism Against Fossil Fuels, a Carbon Concerned Millennial Generation that is Willing to Pay More for Renewable Energy, and for Some Large Electricity Buyers–Attractive Economics
Last week, Oil & Gas 360® published an exclusive interview with Martin Keller, Director of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, the U.S. government’s technical research arm for renewable energy.
In the interview Keller said that he believed that within the next 50 years, renewable energy sources—chiefly wind and solar—would replace fossil fuels as the primary fuels for generating electricity.
“I think fossil fuel will play a role in the future, but I think it will play a different role,” Keller told Oil & Gas 360®. “I think there is a lot of interesting chemistry in oil which we will continue to use in the years to come, but I think there will be different ways and cleaner ways to produce electricity.”
New Data Points to Recent Acceleration of Growth in Renewable Energy Use
According to a report from BCC Research entitled Renewable Energy: Technologies and Global Markets, “in terms of revenue, the global renewable energy market (excluding biofuels) reached $432.7 billion in 2013 and $476.3 billion in 2014. This market is expected to increase to $777.6 billion in 2019, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.3% from 2014 to 2019.”
Recent DOE reports have highlighted the rapid growth of wind and solar. Though their overall share of the energy mix in the U.S. is presently small (5.3%), there is ample evidence that wind and solar penetration are growing across the globe.
In March, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Energy Information Administration (EIA) reported new wind data: “Wind adds the most electric generation capacity in 2015, followed by natural gas and solar. Wind, natural gas, and solar made up almost all new electric generation capacity in 2015, accounting for 41%, 30%, and 26% of total additions, respectively, according to preliminary data.
Some of the forces that are fueling the renewable energy inertia (besides the recent extension of tax credit in the U.S.) is that green energy has won the endorsement of Millennial Generation consumers, a fast growing list of highly visible corporate champions, climate change activists, and governmental bodies led by politicians who are pushing policies to get their jurisdictions off of fossil fuels. All of this fervor towards transitioning to renewable energy is working. It’s moving the needle at an astonishing rate.
Millennials, the Largest U.S. Consumer Group, Increasingly the Driving Force Behind Electric Utility Transformation: Deloitte
Deloitte’s “Resources 2016 Study – Energy Management: Navigating the Headwinds” highlights the increasing influence of millennials aged 21-34, the largest and most dominant consumer group, as a dynamic force behind the shift to cleaner sources of energy – inspired by the desire to reduce their personal carbon footprints, according to a press release from Deloitte issued June 21, 2016.
“The strong desire of residential consumers for clean-energy options, coupled with the increasing cost-effectiveness of solar and wind, are driving growing opportunities for utilities and businesses to explore ways to expand deployment of renewables,” said Marlene Motyka, U.S. alternative energy leader and principal, Deloitte Transactions and Business Analytics LLP. “This trend is really being led by the millennial generation, whose wants and needs are not only relevant, but increasingly an influential factor in the transformation of electricity providers.”
Clean Power Plan Accelerates the Growth of Renewable Generation Throughout United States: EIA
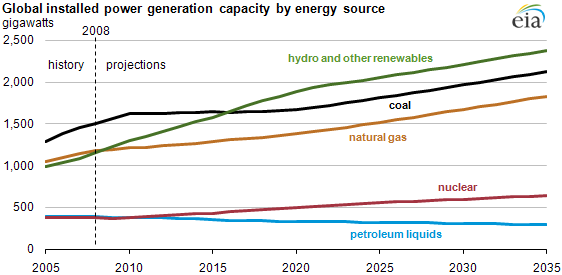
EIA’s Annual Energy Outlook 2016 (AEO2016) Reference case projects that natural gas-fired electricity generation will exceed coal-fired electricity generation by 2022, while generation from renewables—driven by wind and solar—will overtake coal-fired generation by 2029. The shift away from coal-fired generation to a combination of higher natural gas-fired and renewables generation and greater energy efficiency is expected to be accelerated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s Clean Power Plan (CPP).”
Large Companies are Changing How they Acquire Electricity
An article last week by The Motley Fool, entitled Why Corporate America’s Love of Renewable Energy Should Terrify Traditional Utilities, puts it like this: “companies are looking at renewable energy as a way to save costs, lock in rates, and go green, and they may have more power to upset the utility business model than even a million homeowners installing solar panels. The defection of even a small number of large companies from the traditional grid could cause havoc in the utility industry.”
The article makes the economic case for commercial customers to buy renewable energy: “A utility has no ability, or interest, to control commodity costs long-term. If natural gas prices rise, the utility will just pass the cost on to customers, as is its right as a monopoly. But commercial customers want stability and predictability in costs. If they can lock in long-term power purchase agreements from renewable energy, why not lock up the lower cost?
“To put the finances of energy choice into perspective, leaving the grid was so valuable for MGM Resorts (ticker: MGM) that it recently said it will pay $86.9 million [penalty] to leave NV Energy and buy electricity on its own. Seriously, it’s paying nearly $90 million just to cut the cord to the utility. Most customers, like Apple (ticker: AAPL), which is buying energy from third-party plants and building some of its own plants, don’t even have to pay fines, so the economics are even better.
“If the economics didn’t work, commercial customers wouldn’t be looking to buy renewable energy today. But it does, and that’s the biggest reason commercial customers are looking to go renewable. While economics is the real driver of commercial renewable energy projects, the PR boost can’t be bad for companies. They get to call themselves green or say they have a small environmental impact, something companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon have been pushing for years.”
In a story entitled Utilities Pursuing New Business Models, utility expert Erich Gunther talked to Smart Grid News about changes heading to the electric utilities at a rapid clip:
“Does your utility want to anticipate changing circumstances and define its new role or wait until disruptive forces overtake it? One response is to fight change and lobby for the status quo. Another is to do what Southern California Edison has been doing and really take a detailed look at one’s systems and planning processes and figure out how to manage changing circumstances in a way that allows the business model itself to evolve.
“Really, the issue is not whether change is here, but how it’s going to be managed by utilities, how it’s going to be regulated by policymakers and how it’s going to be funded. Utilities will be here in some form or another for a long time. But the benefit of looking ahead and analyzing how a utility’s business model can transition to manage and even take advantage of changing market circumstances is that by doing so, they can define their new role and thrive in the new era that’s upon us.”
Denmark’s Wind Developer DONG Energy Makes the Point
“I have no doubt that costs of offshore wind and solar energy over time will come down and be at same level as fossil fuels,” DONG Energy’s Chief Executive Henrik Poulsen said in an interview with MarineLink. “Our vision is that green energy will be cheaper than conventional energy. It can happen within a decade.”
“Five years ago the price for producing one megawatt was about 160 euros. We expect to reduce that to around 100 euros per megawatt before 2020.”
“It is our clear impression the green transition has a pretty strong momentum. The governments we talk to are committed to reduce CO2 emissions energy.”
Last week, DONG announced the completion of Europe’s largest initial public offering in 2016 – its $15 billion IPO June 13, 2016 – and the initial trading of its shares on Nasdaq Copenhagen. DONG says it has built more offshore wind farms than any other company worldwide. “We have built more than one quarter of the total offshore wind capacity in the market. By 2020, we aim to have doubled our installed capacity compared with 2016 from 3.0 GW to 6.5 GW. The installed capacity in 2020 is equivalent to the annual electricity consumption of 16 million Europeans.” The company says it has 900,000 power and gas customers.
“We can supply 7.5 million Europeans with electricity from our offshore wind farms; compared to 2006, we have reduced the same amount of CO2 as 7 million cars emit in one year.”
But DONG is diversified. In addition to its wind business, in 2015 DONG has oil and gas production that averaged 115,000 BOPD, of which 90 % came from Norwegian fields and 10 % from Danish fields, according to the company. “Our production is equivalent to the annual oil and gas consumption of ten million Europeans.”
Western Governments Are Galloping Toward Renewable Energy
The global PR chops of organizations like the IEA and hundreds of other environmental groups who are singularly focused on climate change are making a difference. They are expert at harnessing the power of public relations, traditional media, movie stars and social media to grab the attention of consumers, companies and governments.
Ontario
This month Ontario released its much anticipated Five Year Climate Change Action Plan 2016-2020. Here is how Ontario Premier Kathleen Wynne launched the province’s 85-page report:
“We know that climate change is real and is happening at an alarming rate. Ontario has a responsibility to tackle the immediate threat — and seize the opportunity — that climate change poses. Our coordinated efforts will protect and improve our way of life, while bolstering the economy and leaving a sustainable legacy for our children and grandchildren. Already we’ve taken strong action by ending dirty coal emissions in our province for good, making unprecedented investments in transit, building an innovative clean technology sector, introducing a cap and trade program that will further drive down emissions and setting aggressive greenhouse gas reduction targets. We are establishing ourselves as global leaders in the fight against climate change. By showing the important role that provinces and regions play in building a low-carbon economy, we are influencing action around the world.”
Canada’s CBC and other Canadian media outlets analyzed the Ontario climate plan, saying it “will provide billions of dollars in subsidies and incentives to businesses and homeowners.”
“The province will spend up to $8.3 billion on a range of programs to encourage people and companies to switch to more energy-efficient heating systems, buy electric or hybrid cars, convert big trucks to natural gas, add more bio-fuel to gasoline, and help the agriculture and industrial sectors adopt low-carbon technologies,” CBC said.
“Most of the money is expected to come from a cap-and-trade program for industrial polluters that the Liberal government expects will raise $1.9 billion a year. All of the cap-and-trade money will go into a dedicated fund for lowering Ontario’s carbon footprint.
“Two groups representing automakers said continued rebates of up to $14,000 for electric vehicles, free overnight charging for four years, and a “cash-for-clunkers” program to get older cars off the roads will help create consumer demand for EVs.
“The rebates, combined with looking at renewable fuels, is sort of a broad-based approach to reducing emissions overall from the transportation sector,” said David Adams, president of Global Automakers of Canada.
“Ontario Premier Kathleen Wynne says the Liberal climate change plan will make the province ‘cleaner and greener,’ but the opposition PCs say it spends money the government hasn’t collected yet.
“Many of the initiatives announced today will help consumers understand that electric vehicles are part of the future, of their future,” said Mark Nantis of the Canadian Vehicle Manufacturers Association.
The Ontario cap-and-trade plan takes effect in January when Ontario joins an existing carbon market with Quebec and California.
Stockholm
“Sweden’s capital joins cities around the world in withdrawing their funds from coal, oil and gas companies,” a European environmental group 350.org said in a press release this week. “The amendment of the city’s investment policy has led to the withdrawal of approximately 30 million SEK from fossil fuel companies.
“ ‘Stockholm’s decision to divest from companies driving the climate crisis demonstrates that it’s no longer morally acceptable to invest in or support business as usual for the fossil fuel industry’, says Andrew Maunder who has campaigned with Fossil Free Stockholm for divestment for over a year.
“Stockholm’s political leaders clearly understand that averting the climate crisis means doing everything in their power to keep any more fossil fuels from being burnt,” the release said.
The website’s “about us” statement says “unless we can reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere to 350 parts per million, we will cause huge and irreversible damage to the earth. But solutions exist. All around the world, a movement is building to take on the climate crisis, to get humanity out of the danger zone and below 350. This movement is massive, it is diverse, and it is visionary. We are activists, scholars, and scientists. We are leaders in our businesses, our churches, our governments, and our schools. We are clean energy advocates, forward-thinking politicians, and fearless revolutionaries. And we are united around the world, driven to make our planet livable for all who come after us.”
USA
Quoting from Whitehouse.gov: “President Obama believes that no challenge poses a greater threat to our children, our planet, and future generations than climate change — and that no other country on Earth is better equipped to lead the world towards a solution.
“That’s why under President Obama’s leadership, the United States has done more to combat climate change than ever before.
“President Obama believes in the need to transition to a cleaner, more reliable and affordable 21st century power grid. Under his leadership, transformations in how we produce and consume electricity are decreasing carbon pollution, scaling up renewable energy, and generating savings on consumers’ energy bills … With this dynamic progress as the backdrop, today the White House is hosting a Summit on Scaling Renewable Energy and Storage with Smart Markets. The Summit brings together regulators, power companies, municipalities, and energy developers that are leading efforts to promote smart electricity markets and greater grid integration of renewable energy and flexible resources such as energy storage.”
California
Two of California’s stated goals, listed as Governor Edmund Brown’s Key Climate Change Strategies, are to increase renewable electricity production to 50% and to cause a 50% reduction in petroleum used by vehicles.
For 2010, the California Department of Motor Vehicles had 23,799,513 driver’s licenses and a total of 31,987,821 registered vehicles traveling up and down California’s highways. With 32 million vehicles on California’s highways at any given time, that’s a lot of gasoline demand that’s going to move over to electricity demand, assuming the electric vehicle industry can successfully extend the usable range per vehicle charge to a close match for the number of miles that cars, vans and SUVs powered by internal combustion engines can drive on a tank of gas.
The IEA put out its Tracking Clean Energy Progress 2016 Report, “which listed EVs among the only three clean energy technologies on track to meet 2025 targets for successful transition to a decarbonised energy system,” the agency said.
Further data from the report: “Electric cars still have just a 0.1% market share worldwide. But they make up more than 1% of the fleet in seven countries, including China, where registrations tripled last year. Norway had the highest share of electric cars, at 23%, followed by the Netherlands, at 10%. The other countries are Sweden, Denmark, France, China and the United Kingdom, while a decline in U.S. electric cars sales pulled the share there down to 0.7%.
“Policy support is the main driver of electric cars’ sales success, Beyond One Million Electric Cars explains. [NOTE: “Beyond One Million Electric Cars” is an IEA report.] Among other incentives, both Norway and the Netherlands reduce registration taxes for EVs and allow them access to lanes barred to other vehicles. Other policy support mechanisms detailed in the Global EV outlook 2016 include fee and toll waivers, both on the road and for parking, and tailpipe emission standards.”
San Francisco
San Francisco will be the first major U.S. city to require new buildings to have solar panels installed on the roof. According to a story by NPR, residential and commercial buildings 10 stories or shorter will be required by the new law to install some form of solar energy — either electricity-generating panels or solar heating units. “It’s a step toward San Francisco’s goal of meeting the city’s electrical demands with 100 percent renewable energy,” the sponsor noted.
The ordinance was passed unanimously by the city’s board of supervisors in April.
A Perfect Marriage
The very large, very well-funded global energy policy organizations like the IEA are totally engulfed in the push to adopt renewable energy to combat climate change. “It is a great honour for the IEA to be asked to take on this prestigious role, given the stature of the CEM and the importance of its initiatives,” IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol, said in a press release announcing a proposal by the 7th Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) that the IEA serve as the home of a new, multilateral CEM Secretariat starting later in 2016. “The CEM’s position as a global platform to support collaboration and promote the adoption of clean energy policies dovetails perfectly with the IEA’s emergence as a clean energy hub – it represents a perfect marriage.”
Corporate Momentum: Companies Can’t Climb Onboard Fast Enough
Many legacy consumer brands and global firms with international visibility are jumping onto the “all-out for renewables” bandwagon.
NEWSWEEK’S TOP 20 GREEN COMPANIES FOR 2016
Rank Score Company Industry
| 1 | 87.70% | Shire PLC | Ireland | Health Care |
| 2 | 83.90% | Reckitt Benckiser Group PLC | United Kingdom | Consumer Staples |
| 3 | 83.20% | BT Group PLC | United Kingdom | Telecommunication Services |
| 4 | 82.90% | Swisscom AG | Switzerland | Telecommunication Services |
| 5 | 82.00% | Essilor International SA | France | Health Care |
| 6 | 81.90% | NIKE Inc | United States | Consumer Discretionary |
| 7 | 81.80% | Unilever PLC | United Kingdom | Consumer Staples |
| 8 | 80.70% | Sky PLC | United Kingdom | Consumer Discretionary |
| 9 | 79.60% | Siemens AG | Germany | Industrials |
| 10 | 78.80% | Schneider Electric SE | France | Industrials |
| 11 | 78.70% | Biogen Inc | United States | Health Care |
| 12 | 78.60% | Enbridge Inc | Canada | Energy |
| 13 | 78.40% | Ecolab Inc | United States | Materials |
| 14 | 77.30% | Airbus Group NV | France | Industrials |
| 15 | 76.60% | Commonwealth Bank of Australia | Australia | Financials |
| 16 | 76.40% | MetLife Inc | United States | Financials |
| 17 | 75.80% | Oracle Corp | United States | Information Technology |
| 18 | 75.80% | Koninklijke Philips NV | Netherlands | Industrials |
| 19 | 75.60% | Johnson & Johnson | United States | Health Care |
| 20 | 74.80% | Credit Agricole SA | France | Financials |
Schneider Electric just about broke its own arm patting itself on the back in these press release headlines last week: “Schneider Electric rises to 10th place in the Newsweek Global Green Ranking 2016”
“Company leapfrogs to 10th place from 25th in 2015 – New ranking a testament of company’s vision to produce technologies that ensure Life Is On everywhere, for everyone, at every moment – The ranking progression also acknowledges the commitments taken by the company at COP21”
The slate of global companies who are investing resources to promote green energy and the use of renewables is growing by the day, and they want to make sure their customers and potential customers know they are all about green energy.
Here are some other recent headlines:
“Honeywell Awards 50 Teachers from Around the World Scholarships to Attend Green Boot Camp – Hands-on workshop in San Diego provides middle school educators with tools to teach energy, sustainability and environmental concepts. One teacher who participated in the Green Boot Camp last year said, “From building wind turbines to learning about renewable energy initiatives in our own state, I’ve been able to better educate my students on important topics and concepts, and I’m grateful for Honeywell’s support.”
“Toyota Motor North America Commits to 100% Renewable Energy Contract with MP2 Energy -Five-year electricity supply deal includes 7.75 MW from on-site solar generation”
“Toyota Motor North America just contracted to buy 100 percent renewable energy for Toyota’s new North American headquarters in Plano, Texas. The contract with MP2 Energy for Toyota’s 2.1 million square-foot campus also supports 7.75 megawatts of on-site solar generation at the new headquarters. The company said the renewable energy for Toyota will be sourced from various resources including local Texas wind and offsite solar.”
Last fall, Starbucks, Wal-Mart, Goldman Sachs and Johnson & Johnson were described by CNBC as latecomers when they joined other well-known global companies making a formal pledge to convert 100% to renewable energy. This signaled a strong push for corporate backing of cleaner sources of power, according to a CNBC special report on sustainable energy.
The four “latecomers” joined nine organizations and 36 corporations who have signed a pledge to cut their carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by deriving their electricity consumption solely from renewable energy sources. The company pledge comes from The Climate Group’s global initiative “RE100”.
IKEA, Nestle, Amazon and Siemens are on the RE-100 bandwagon with companies like Johnson & Johnson which aims to be 100 percent renewable by 2050. According to the CNBC report, other companies’ targets “include Goldman Sachs (100% renewable by 2020); Nike (100% by 2025); Procter & Gamble, (30 percent renewable by 2020); Steelcase (which became 100 percent renewable in 2014).
Two Generations of School Kids are Bringing their Green Energy Lessons into the Voting Booth
We’re on the second, possibly third, generation of school children who have been taught from Kindergarten through college that fossil fuels cause problems, and that renewable energy is the solution. Now these are the adults who vote for policymakers in their local, state and national governments.
As all this inertia causes more states, provinces, and countries to begin to impose stricter limits on amounts of carbon emitted, they will continue to create policies that result in even more widespread demand for renewable energy. If it grows to the point of what today’s policymakers want—the end of fossil fuels—the demand for fossil fuels is going to eventually follow suit and decline. But when?
The switch may come sooner than the industry thinks.
Bloomberg published a story recently under the title Big Oil’s Footprint in Washington Shrinks with Price of Crude. The story addresses how the commodities downturn is shrinking the budgets of the petroleum industry for tasks like lobbying its cause with Washington policy makers. The story looks at the effect this will have on government policies that favor renewables over coal, oil and natural gas. “[Because oil and gas companies’ ‘economic fortunes are very closely tied to policy around climate change, this is an industry with a tremendous amount at stake’, said Lee Drutman, a senior fellow at the think tank New America who analyzes corporate influence and political spending,” Bloomberg reported. “The industry ‘is facing a number of almost existential threats’ and is ‘going to be directly affected by public policy choices in the next several years’.”
Large Utilities are Adding Renewable Generation Capacity at a Rapid Clip
Duke Energy, which already operates 34 solar facilities in North Carolina, announced the addition of a new solar plant in June. “With 670 miles of wire and cable and 487,000 solar panels, Duke Energy’s (ticker: DUK) 40-megawatt Elm City Solar Facility is the latest addition to the company’s renewable portfolio to power a clean energy future. … The plant began operations in March and is currently supplying energy to customers. The facility is the newest solar site that Duke Energy owns and operates in North Carolina. Overall, Duke Energy has 35 solar facilities across the state.”
The Elm City Solar Facility in Wilson County has an expected annual output of 82,000 megawatt-hours –roughly what 7,000 residential customers would use in a year, according to a company press release. In total, Duke says its companies have installed about 450 MW of solar energy in the state, enough to power 85,000 average homes at peak production. In a statement Duke said it has invested more than $4 billion in renewable energy since 2007 and plans to invest about $3 billion over the next five years.
At Half the Carbon, Natural Gas is the Logical Replacement for Coal—or Is It?
Power companies are adding combined cycle natural-gas fired power plants in lieu of new coal plants, or coal plant environmental retrofits. For the first time natural gas is outpacing coal for electrical power generated in the U.S. Even more telling, CO2 emissions were the lowest since 1993 because of the switch from coal to gas to make electricity. Burning natural gas emits about half as much carbon dioxide as burning coal.
But, even as fast as new natgas power plants are being built and commissioned, for 2015 the number one source of new generation capacity was not natural gas. It was wind.
The following data is from the EIA:
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Preliminary Monthly Electric Generator Inventory
Note: Data include facilities with a net summer capacity of one megawatt and above.
Wind. Wind installations steadily increased in 2014 and 2015 from less than 1,000 megawatts (MW) added in 2013. Uncertainty surrounding the extensions and modifications of the federal production tax credit (PTC) over the past several years led to large fluctuations in annual wind additions. The record amount of additions in 2012 was followed by a precipitous drop-off in 2013 and a subsequent rebound in 2014 and 2015—a pattern also visible with previous years’ PTC expiration and renewal cycles.
Texas added the most wind capacity (42% of total wind additions), followed by Oklahoma, Kansas, Iowa, and North Dakota. All of these states are located in the central part of the country, where wind resources are the strongest. In Texas, new wind power records are continuously being set as the wind fleet continues to grow.
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Preliminary Monthly Electric Generator Inventory
Note: Data include facilities with a net summer capacity of one megawatt and above.
Natural gas. Natural gas additions, mainly combined-cycle plants, were lower in 2015 than in recent years. New Jersey and Texas together made up half of all natural gas additions.
In New Jersey, most of the new capacity came from two combined-cycle plants, the Newark Energy Center (685 MW) and the Woodbridge Energy Center (795 MW). Both plants will be supplied by the Transco natural gas pipeline, which recently completed expansions to bring larger volumes of Marcellus natural gas to market areas.
In Texas, the second phase of the combined-cycle Panda Temple Power Station (734 MW) and three combustion turbine plants totaling 716 MW (Ector County Energy Center, Montana Power Station, and Elk Station) came online.
Utility-scale solar. California added more than 1,000 MW each of utility-scale and distributed solar PV capacity, accounting for 42% of overall solar additions in 2015. North Carolina added 720 MW of utility-scale PV, more than double the amount added in the state in the previous year. In Nevada, the 110 MW Crescent Dunes concentrating solar thermal plant with energy storage came online in 2015 along with several solar PV plants totaling 236 MW.
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Electric Power Monthly
Note: All data reported in alternating-current megawatts (MWAC).
Distributed solar PV. Distributed PV saw significant growth in 2015, particularly in the residential sector, where total installed capacity rose much faster over the year than in the industrial or commercial sectors. While still far behind top distributed solar PV states, several states saw notable growth in 2015, including Nevada, where distributed PV capacity more than doubled from 49 MW to 129 MW. Further growth of Nevada’s distributed PV sector, however, is uncertain because Nevada’s Public Utility Commission recently approved several changes to the net-metering tariffs, including phasing in lower net-metering compensation rates and higher monthly fixed charges for distributed PV customers. These changes are an effort to address concerns about grid maintenance costs being shifted disproportionately from customers with solar systems to non-solar customers.
Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, Preliminary Monthly Electric Generator Inventory
Note: Data include facilities with a net summer capacity of one megawatt and above except for solar, which also includes small-scale distributed solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity. All data reported in alternating-current megawatts (MWAC).
NREL Director Martin Keller put it like this: “I see that in the U.S., we are very blessed discovering all this natural gas. I see that this is a tremendous transition fuel which buys us more time. It’s much cleaner than coal but it of course emits CO2, so in the long run I think we need to find a way to wean ourselves off of fossil fuel. Fifty years out, I don’t think that we would burn natural gas or oil to create electricity.”
U.S. Electricity Generation by Source - 2015
Major energy sources and percent share of total U.S. electricity generation in 2015:
Coal = 33%
Natural gas = 33%
Nuclear = 20%
Hydropower = 6%
Biomass = 1.6%
Geothermal = 0.4%
Solar = 0.6%
Wind = 4.7%
Petroleum = 1%
Other gases = <1%
(Source: EIA –based on generation by utility-scale facilities)